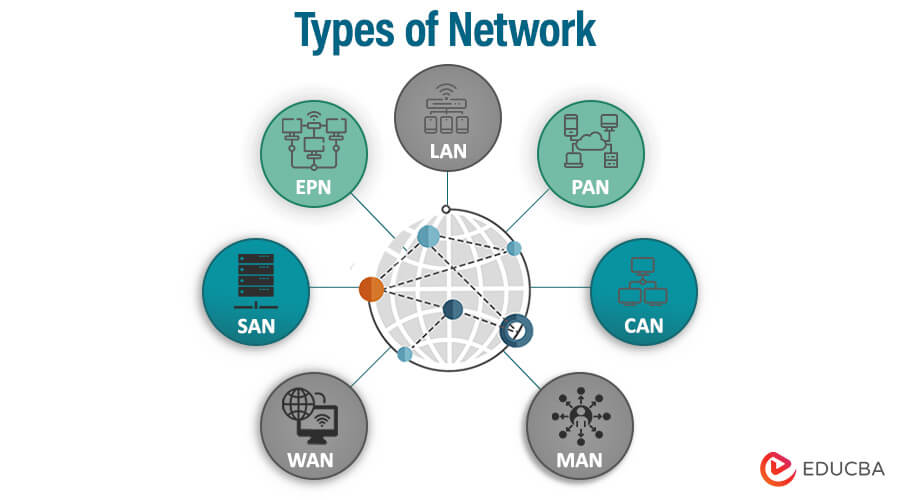
Types of Computer Network
Computer networks are categorized based on their size, scope, and purpose. Here are the primary types:
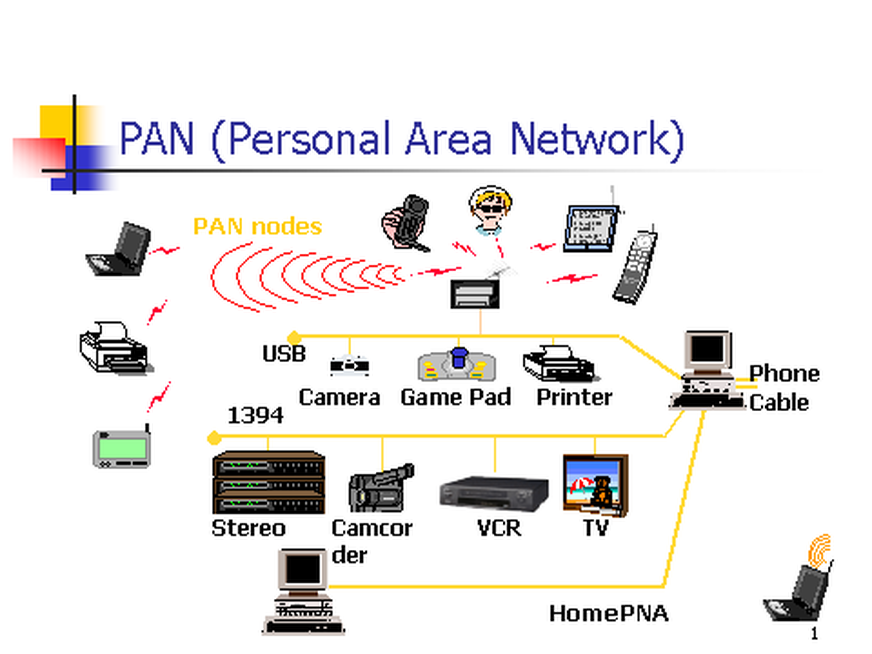
1.Personal Area Network (PAN):-
- Range:Small area,in meters
- Usage:Device that a person uses on himself,like smartphones.laptops,printers,etc.
- Example:Bluetooth,USB connection.
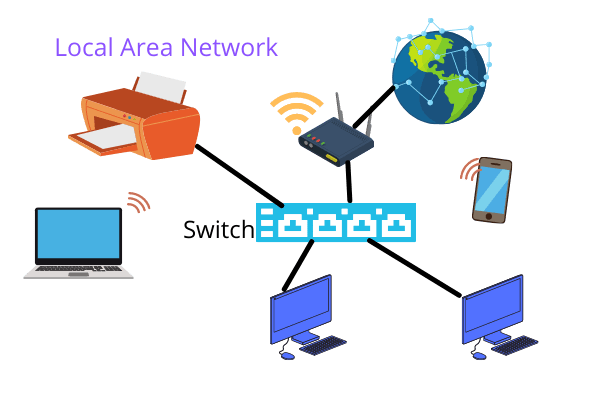
2.Local Area Network (LAN):-
- Range:geographical range that is small like a house,office,or a building.
- Usage:For the computers and the devices which are used by a few individuals in a geographic area.
- Example:Office networks,school network.
3.Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN):-
- Range:Same as LAN but using radio waves like wi-Fi.
- Usage:It enables devices to be connected wirelessly within a restricted range.
- Example:Home Wi-Fi Networks.
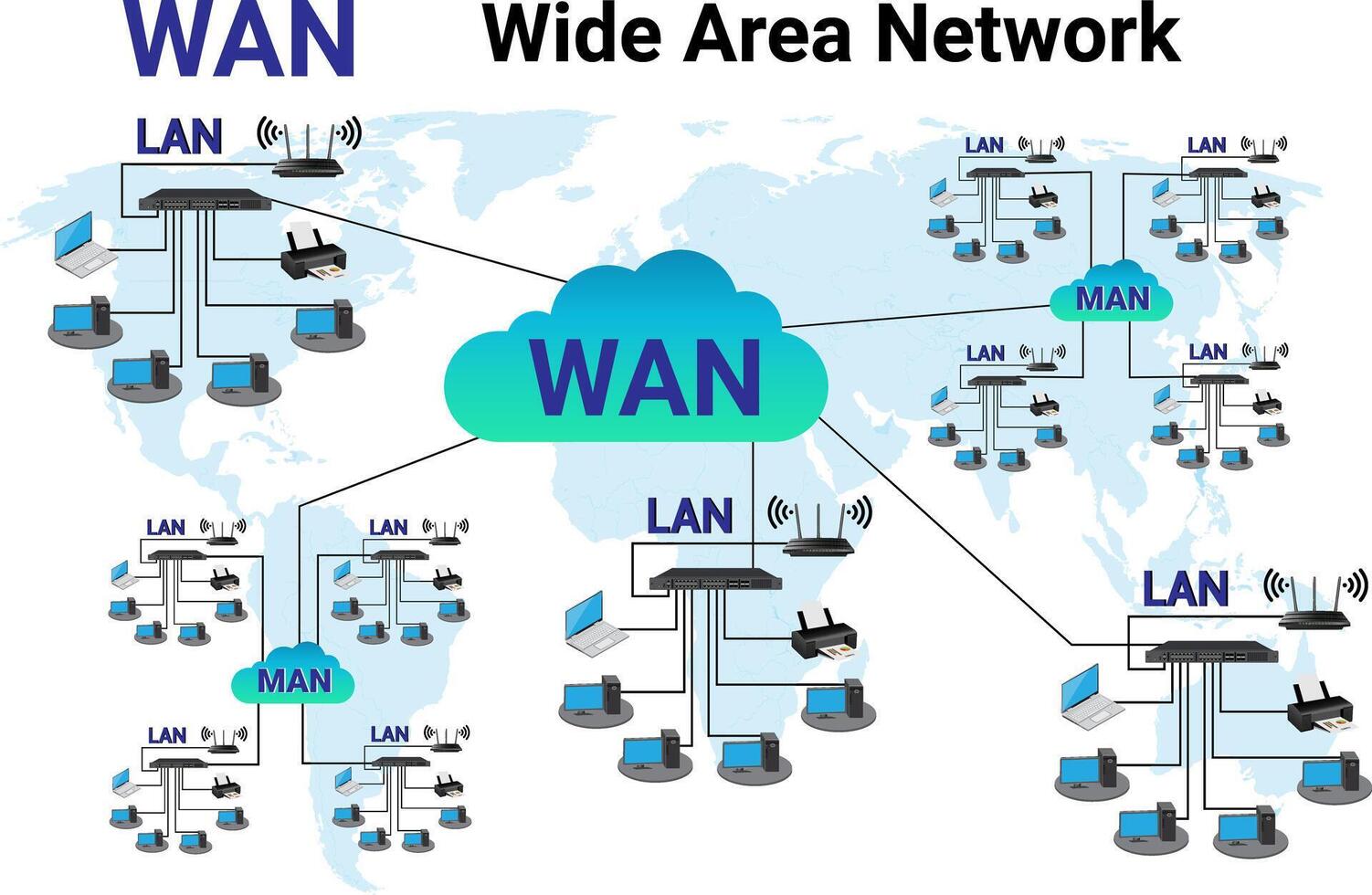
4.Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):-
- Range: Covers an entire city or a whole campus.
- Usage: Juxtaposes multiple LANs to make a bigger network.
- Example: City-wide Wi-Fi or campus network of universities.
5.Wide Area Network (WAN):-
- Range: Reaches out to a large geographical area,extending to different countries or Continents.
- Usage: Connects multiple LAN and MAN over long distance.
- Example: The internet corporate global networks.
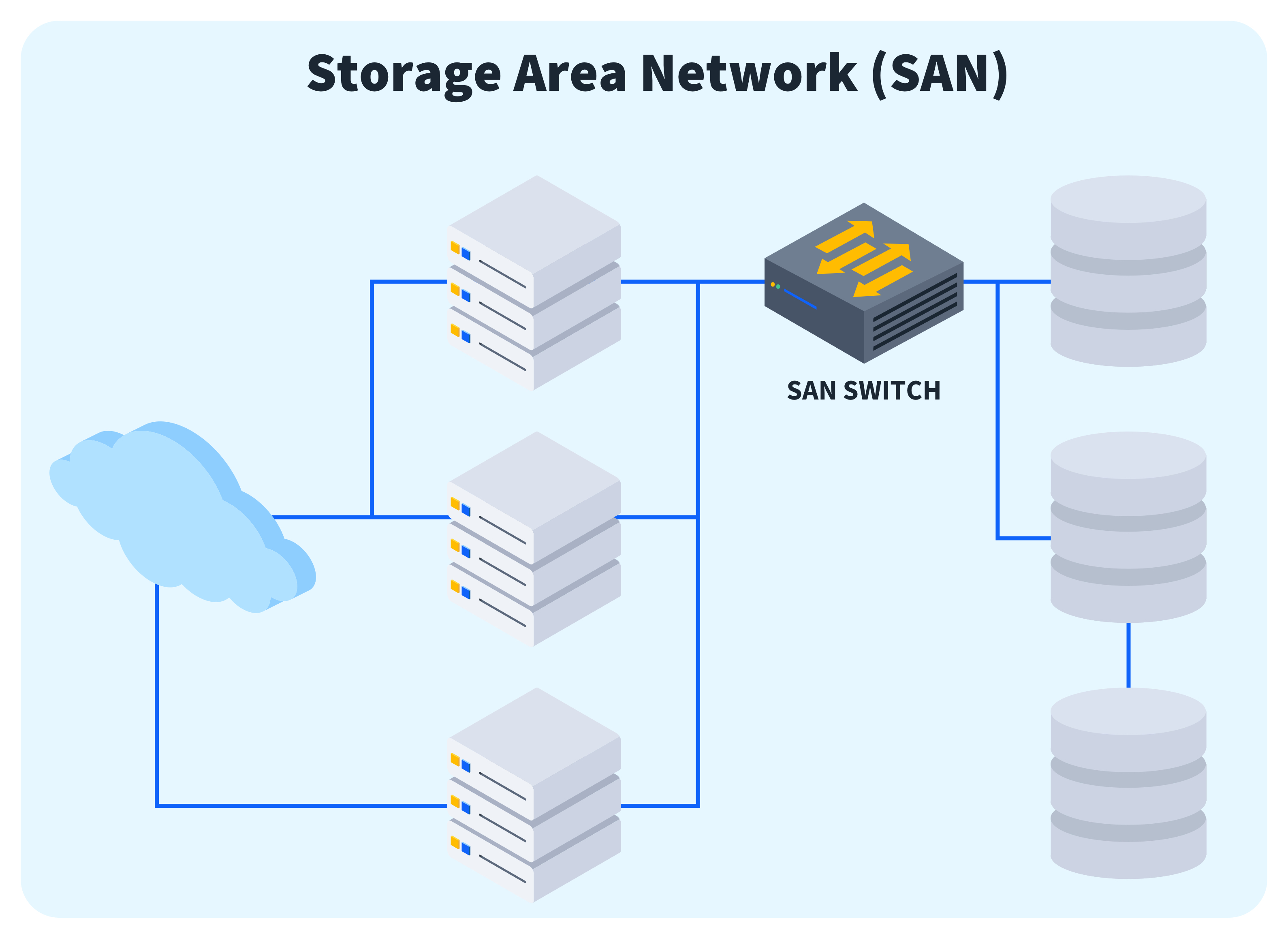
6. Storage Area Network (SAN):-
- Range: Dedicated for data storage devices.
- Usage: Offers access to centralized, block-level storage of data.
- Example: Data center networks.
7.Virtual Private Network (VPN):-
- Range: Virtual network on the internet.
- Usage: Creates secure connectivity to access a private network remotely.
- Example: Remote working connectivity.
8.Campus Area Network (CAN):-
- Range: It spans various buildings within a campus or close geographical location.
- Usage: Often utilized by universities or business campuses.
- Example: University campus networks.
9.Enterprise Private Network (EPN):-
- Range: It is solely used for businesses.
- Usage: Links different branches securely.
- Example: Corporate networks with data centers.
10.Global Area Network (GAN):-
- Range: Global area covered using satellite or fiber optics.
- Usage: Used for communications all over the world.
- Example: Global banking networks.


Comments
Post a Comment