Developing Multimedia
Multimedia developing is the creation and integration of different types of media using text, images, audio, video, and animations into a specific format for communication, education, entertainment, or other purposes.
Multimedia Development Process:-
1.Planning
- Describe goals, target audience, and type of multimedia to be produced.
Create - Create storyboard or script for visualization and flow of content.
- Write text, visuals, and audio according to the structure planned.
- Design and edit using relevant software tools.
- Integrate all media elements using software or platforms.
- Ensure design and theme remain consistent.
- Verify functionality, compatibility (device or browser), and user experience.
Optimize performance - Optimize performance through compression of files without quality loss.
- Publish the multimedia project online (websites, apps) or offline (CD/DVD, USB).
- Distribute via appropriate channels, like social media or email campaigns.
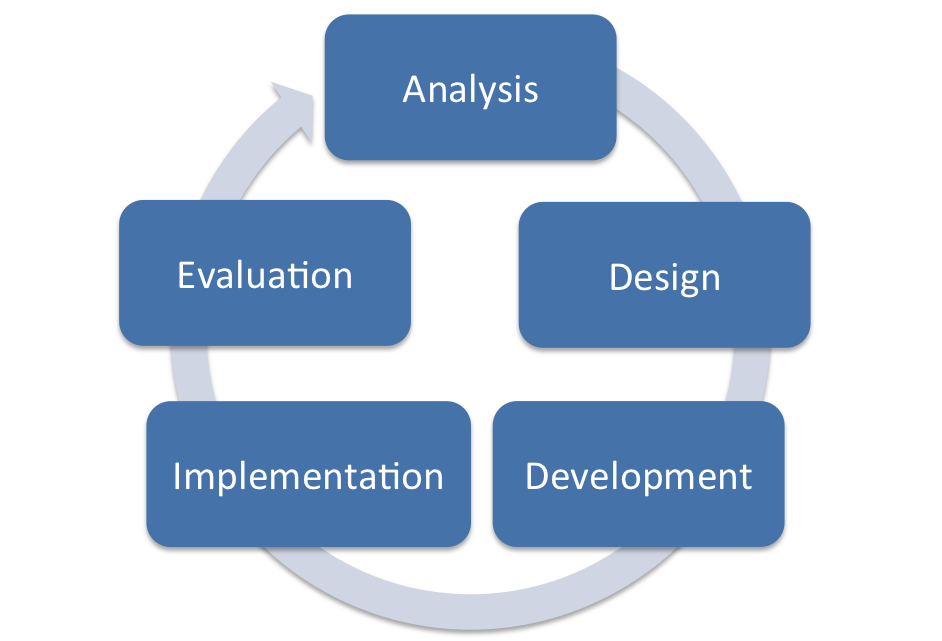
ADDIE Model of Multimedia Development:-
The ADDIE model is an instruction design framework widely used in multimedia development. It stands for Analyze, Design, Develop, Implement, and Evaluate, providing a step-by-step method for preparing effective multimedia content.
- Analyze:-
Objective: Know the needs, goals, and audience.
- Design:-
Objective: Make a thorough plan for the multimedia content.
- Develop:-
Objective: Construct and put together the multimedia content.
- Implement:-
Objective: Deliver the multimedia content to the target audience.
- Evaluate:-
Objective: Measure the effectiveness and usability of the multimedia content.
1.Usability Principles
- Consistency: Keep the navigation, layout, and interactions throughout the application consistent.
- Clarity: Clear labels, instructions, and icons should help guide users.
- Visual or auditory feedback confirming user actions, such as button clicks or form submissions.
- Error Recovery: Design intuitive recovery of errors by users, for example, the facility to undo operations or error messages.
2.Visual Design
- Balance and Layout: Work with grids and alignment to create the visually balanced interface. And avoid clutter by giving every element enough space.
- Typography: Use readable fonts, proper sizes, and adequate contrast between text and background.
- Color scheme: Harmonious color schemes should be applied according to the content and follow the standards for accessibility- WCAG guidelines.
- Use multimedia placement with videos, images, and audio controls to increase understanding and aesthetics but do not overwhelm the user.
3. Navigation
- Intuitive structure: The navigation system must be logical and easy to follow.
- Provides robust search functionality, especially for very large multimedia systems.
- Breadcrumbs: Help users keep track of their location within the application with visual cues, such as breadcrumbs.
- Accessible Controls: Use easily recognizable navigation buttons and keep them within reach.
4. Multimedia Integration
- Optimized media files: Compression of multimedia elements to ensure fast loading without losing quality.
- Playback Controls: Provide play, pause, rewind controls along with volume control for the audio and video content.
- Synchronization: Multidimensional elements such as subtitles and animations should be perfectly synchronized.
- Accessibility Features Videos require captions, audio features need transcripts, and images need alternative text.
5. Accessibility
- Keyboard Interface: All interactive elements should be accessible through keyboard access.
- Screen reader compatibility: In this, multimedia interfaces should seamlessly interact with screen readers.
- Colorblind Accessibility: Avoid relying solely on color to convey information; use patterns or text as supplements.
Need Help In ICT Contact us Now:-https://bizkranti.com/



Comments
Post a Comment